alphaShape
Polygons and polyhedra from points in 2-D and 3-D
Description
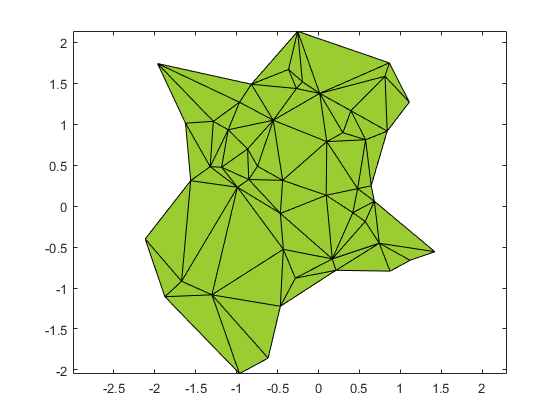
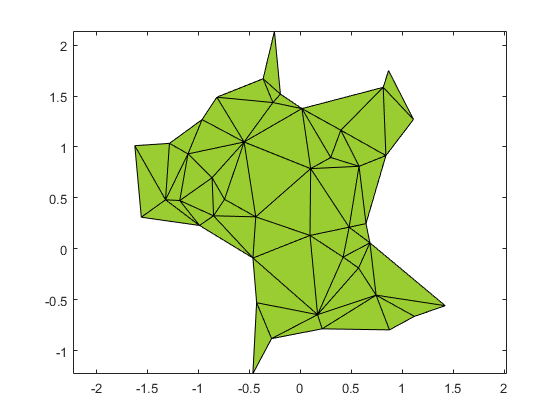
An alphaShape creates a bounding area
or volume that envelops a set of 2-D or 3-D points. You can manipulate
the alphaShape object to tighten or loosen the fit
around the points to create a nonconvex region. You can also add or
remove points or suppress holes or regions.
After you create an alphaShape object, you
can perform geometric queries. For example, you can determine if a
point is inside the shape or find the number of regions that make
up the shape. You can also calculate useful quantities like area,
perimeter, surface area, or volume and plot the shape for visual inspection.
Create Object
Create an alphaShape using the alphaShape function.
Properties
Object Functions
alphaSpectrum |
Alpha values giving distinct alpha shapes |
criticalAlpha |
Alpha radius defining a critical transition in the shape |
numRegions |
Number of regions in alpha shape |
inShape |
Determine if point is inside alpha shape |
alphaTriangulation |
Triangulation that fills alpha shape |
boundaryFacets |
Boundary facets of alpha shape |
perimeter |
Perimeter of 2-D alpha shape |
area |
Area of 2-D alpha shape |
surfaceArea |
Surface area of 3-D alpha shape |
volume |
Volume of 3-D alpha shape |
plot |
Plot alpha shape |
nearestNeighbor |
Determine nearest alpha shape boundary point |
Examples
See Also
Introduced in R2014b
Was this topic helpful?